Revenue Cloud Developer Roadmap
With CPQ entering End of Sale, Revenue Cloud skills are in demand. But the skills you actually need depend on what you’re trying to do. This guide covers what matters for real Revenue Cloud work, not a certification checklist, but the practical skills that make implementations successful.
Core Revenue Cloud Skills
These are the areas you’ll spend most of your time on:
Product Catalog Management
The product catalog is the foundation of everything in Revenue Cloud. You need to understand:
- Catalog and category structure - How products are organized and browsed
- Product and bundle configuration - Building products with options, features, and constraints
- Attribute management - Defining product attributes and how they drive behavior
- Selling models - One-time, subscription, usage-based, and hybrid models
- Product classifications - How products inherit attributes and behaviors
This is where most of the configuration work happens. Get comfortable with the Product Catalog Management app and understand the data model.
Pricing
Pricing in Revenue Cloud works differently than CPQ. The key concepts:
- Pricing procedures - The logic that calculates prices (replaces CPQ price rules)
- Pricing waterfall - Understanding the sequence of price calculations
- Discount and promotion rules - How discounts are applied and controlled
- Context definitions - How pricing adapts to different scenarios
The Revenue Cloud Developer Guide covers the pricing architecture in detail.
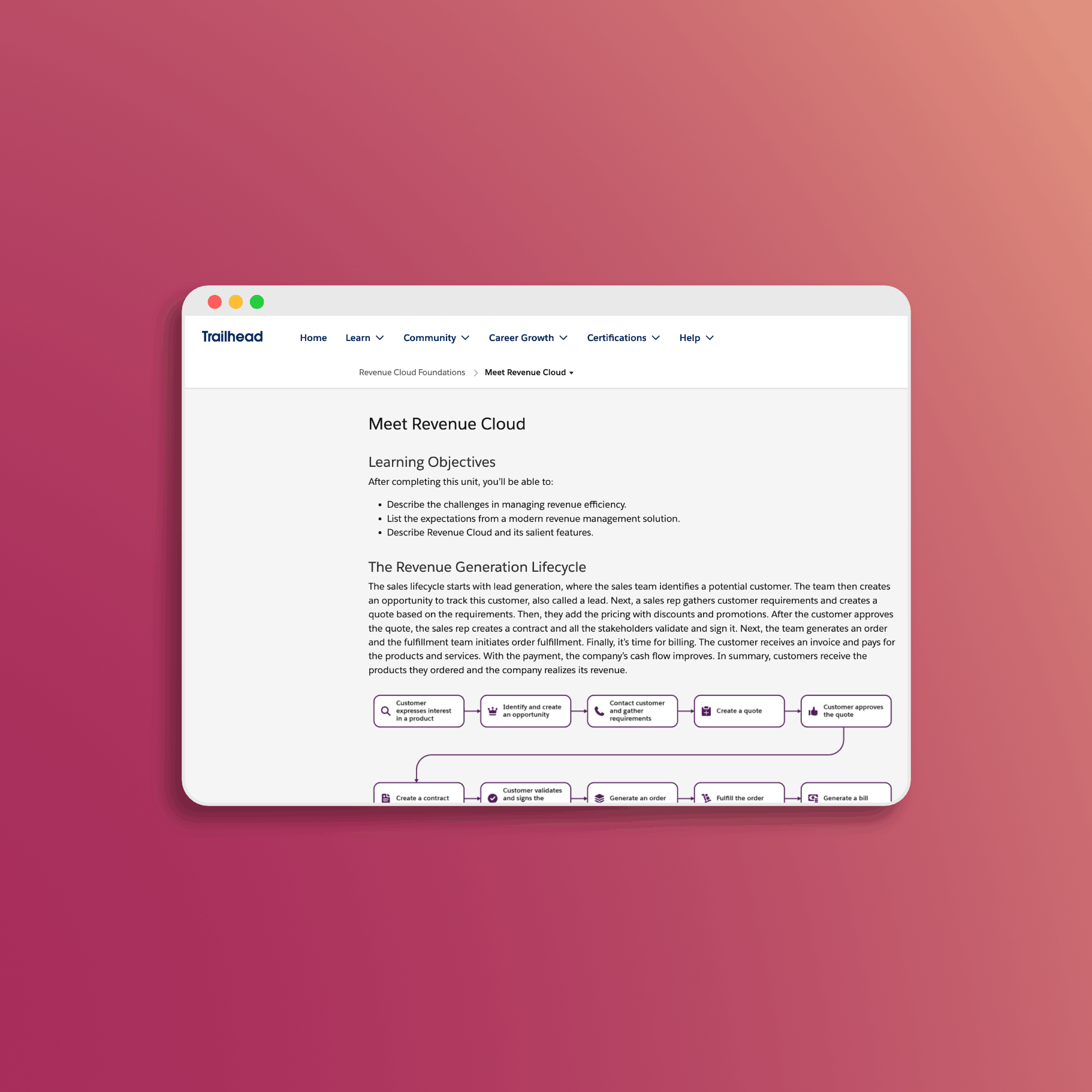
Quote-to-Cash Process
Understanding the end-to-end flow:
- Quote creation and management - The quoting workflow and user experience
- Approval processes - How deals get approved
- Document generation - Producing quotes and contracts
- Order processing - Converting quotes to orders
- Contract management - Amendments, renewals, and lifecycle
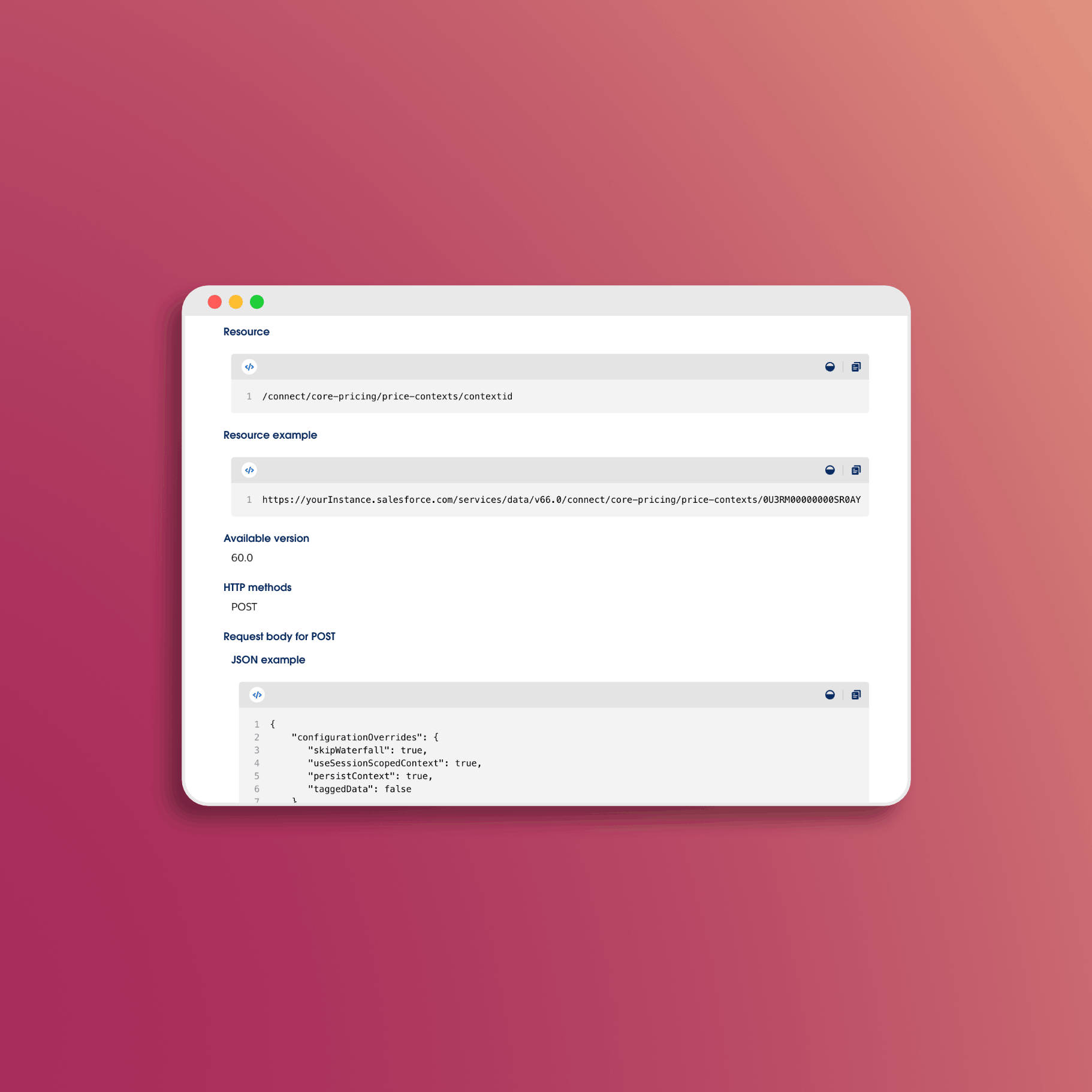
Revenue Cloud APIs
For any custom development or integration work, you need to understand the APIs:
- Pricing Business APIs - Programmatic pricing calculations (documentation)
- Product Configurator APIs - Headless product configuration (documentation)
- Standard Salesforce REST APIs - For working with Revenue Cloud objects
The APIs are available in API version 60.0 and later. If you’re building integrations or custom experiences, start with the API tutorial.
What About CPQ Knowledge?
If you’re coming from CPQ, a lot translates:
- Product bundles → Product bundles (similar concepts, different implementation)
- Price rules → Pricing procedures
- Quote Line Editor → Still exists, modernized
- Calculator API → Pricing Business APIs
The mental model is similar, but the technical implementation is different. CPQ experience gives you a head start on understanding the business problems Revenue Cloud solves.
What About Certifications?
Salesforce offers relevant certifications (CPQ Specialist, OmniStudio Developer, Industries CPQ Developer), but I’ll be honest: certifications test isolated knowledge in controlled scenarios. Real Revenue Cloud implementations involve:
- Integration with ERP, billing, and other systems
- Data migration from legacy platforms
- Custom requirements that don’t fit standard patterns
- Performance tuning with real data volumes
- Working alongside non-Salesforce products
Certifications can validate foundational knowledge and help with job applications, but they don’t prepare you for the messiness of real projects. Focus on hands-on experience over collecting credentials.
Consultant vs. End-User Organization
The skills you need depend on your role:
Implementation consultants need broad exposure—multiple implementations, different industries, migration strategies, and the ability to adapt patterns to new situations. You’ll see more variety but less depth in any single org.
Revenue Cloud specialists at end-user organizations go deep on one implementation. You’ll know your product catalog intimately, understand the specific business rules, and own the ongoing optimization. You’ll also deal more with integrations to internal systems and cross-functional stakeholders.
Both paths are valid. Consultants often start at partners and move in-house; internal specialists sometimes move to consulting for broader exposure.
Learning Resources
Free Resources
Trailhead:
Salesforce Documentation:
- Revenue Cloud Developer Guide
- Revenue Cloud Help Articles
- Release Notes - Revenue Cloud evolves quickly
Hands-On Practice:
- Set up a Developer Edition or Promo Edition org and build something
- Work through the product catalog setup end-to-end
- Create pricing procedures and test them with real scenarios
Continued Learning
Revenue Cloud is evolving rapidly, new features ship each release, and best practices are still emerging. Subscribe to my newsletter ‘Learn Revenue Cloud’ at the bottom of the page for real-world insights, implementation patterns, and updates as the platform matures.
Conclusion
Revenue Cloud skills come down to understanding the product catalog, pricing engine, and quote-to-cash process. The APIs matter if you’re doing custom work. Everything else (OmniStudio, advanced billing, complex integrations) you can learn as needed for specific projects.
Start with a trial org, build a product catalog, configure some pricing, and generate a quote. That hands-on experience is worth more than any certification prep course.
📅 Let's Work Together!